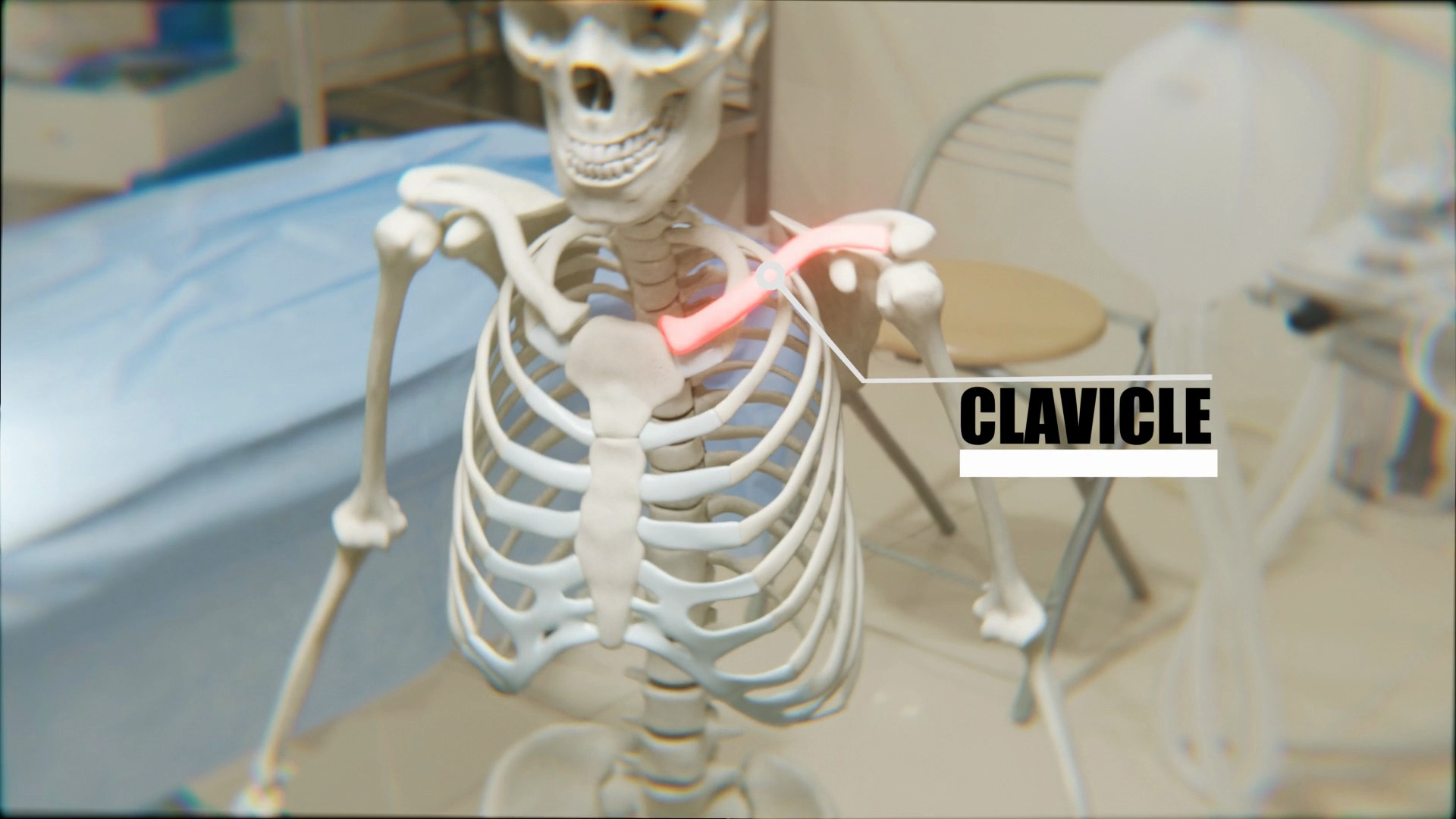
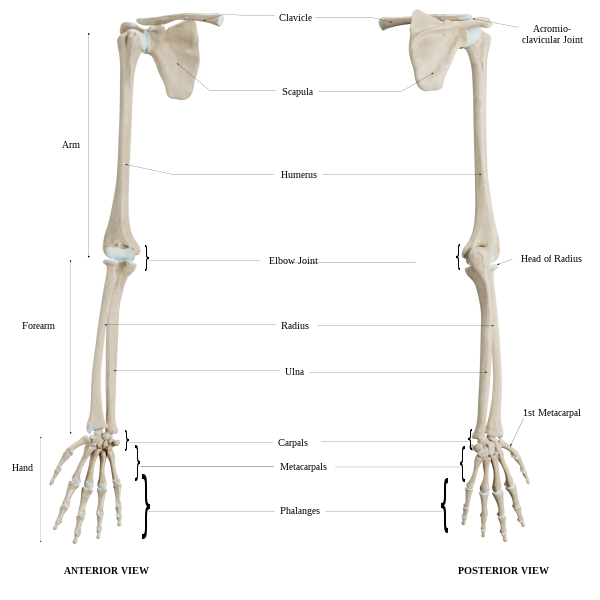
Humerus 3d Anatomy
Anatomy of Humerus
The Humerus is the largest bone of the upper limb and it has two ends and a shaft. The proximal end is round and has an articular head. The distal end is irregular in shape. The shaft connects both the proximal and distal ends.
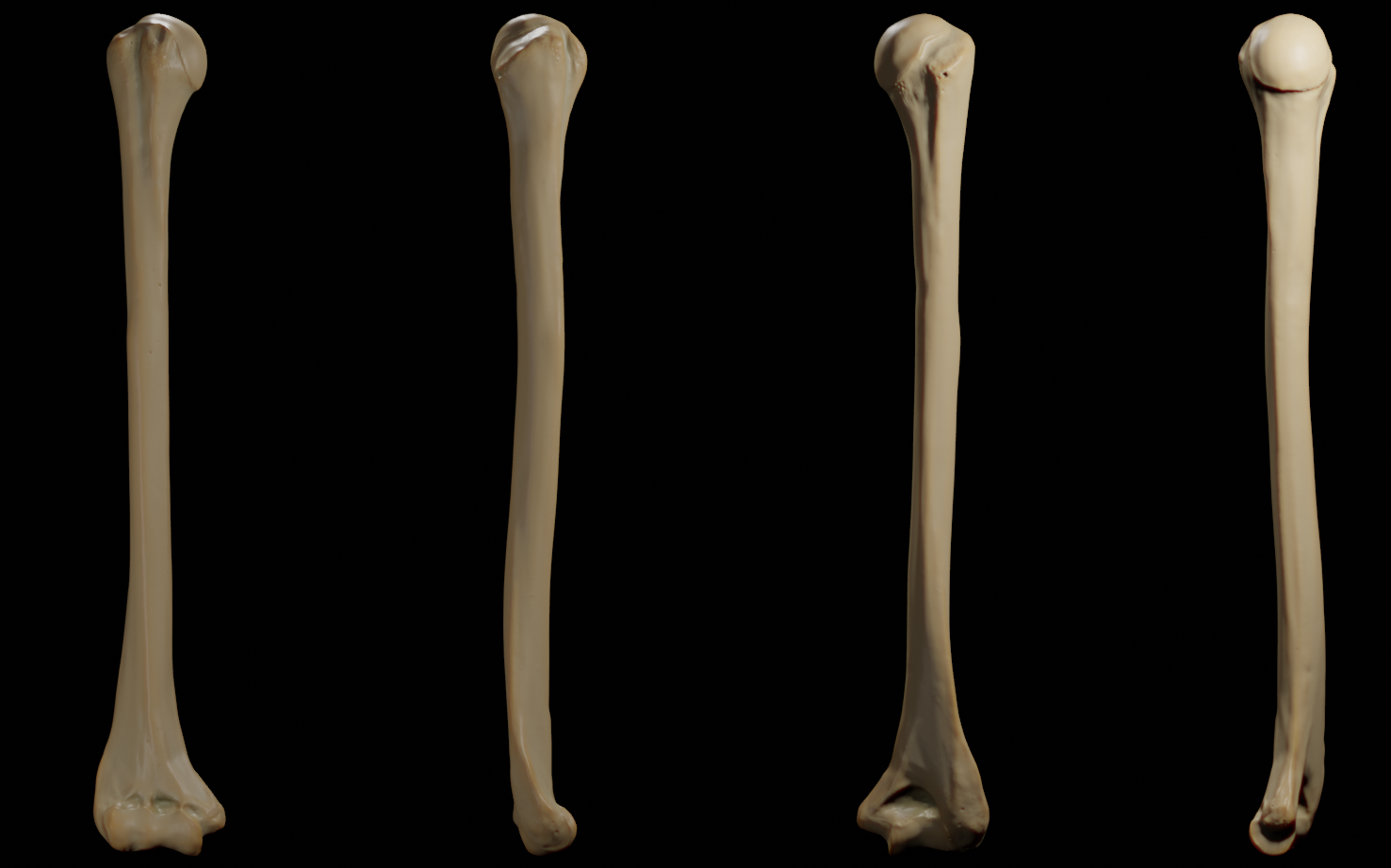
Head of the humerus
The head of the humerus is a hemisphere that faces medially and articulates with the glenoid fossa of the shoulder joint.

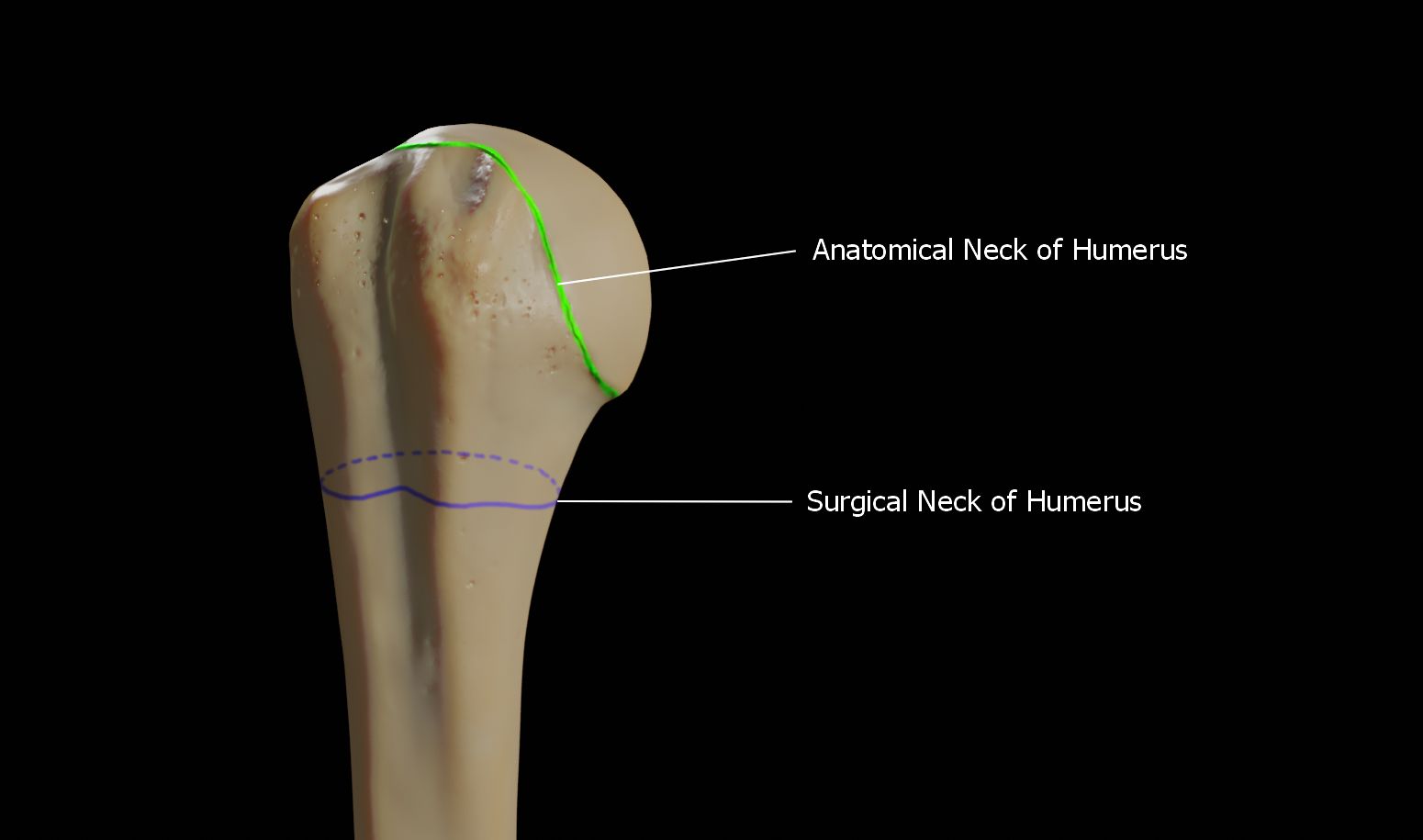
Neck of the Humerus
The anatomical neck is the groove that surrounds the articular surface of the head of the humerus. This is where the joint capsule is attached. The surgical neck however, is a segment present inferior to the humeral head. This acts as a connection between the head and the shaft of the humerus.
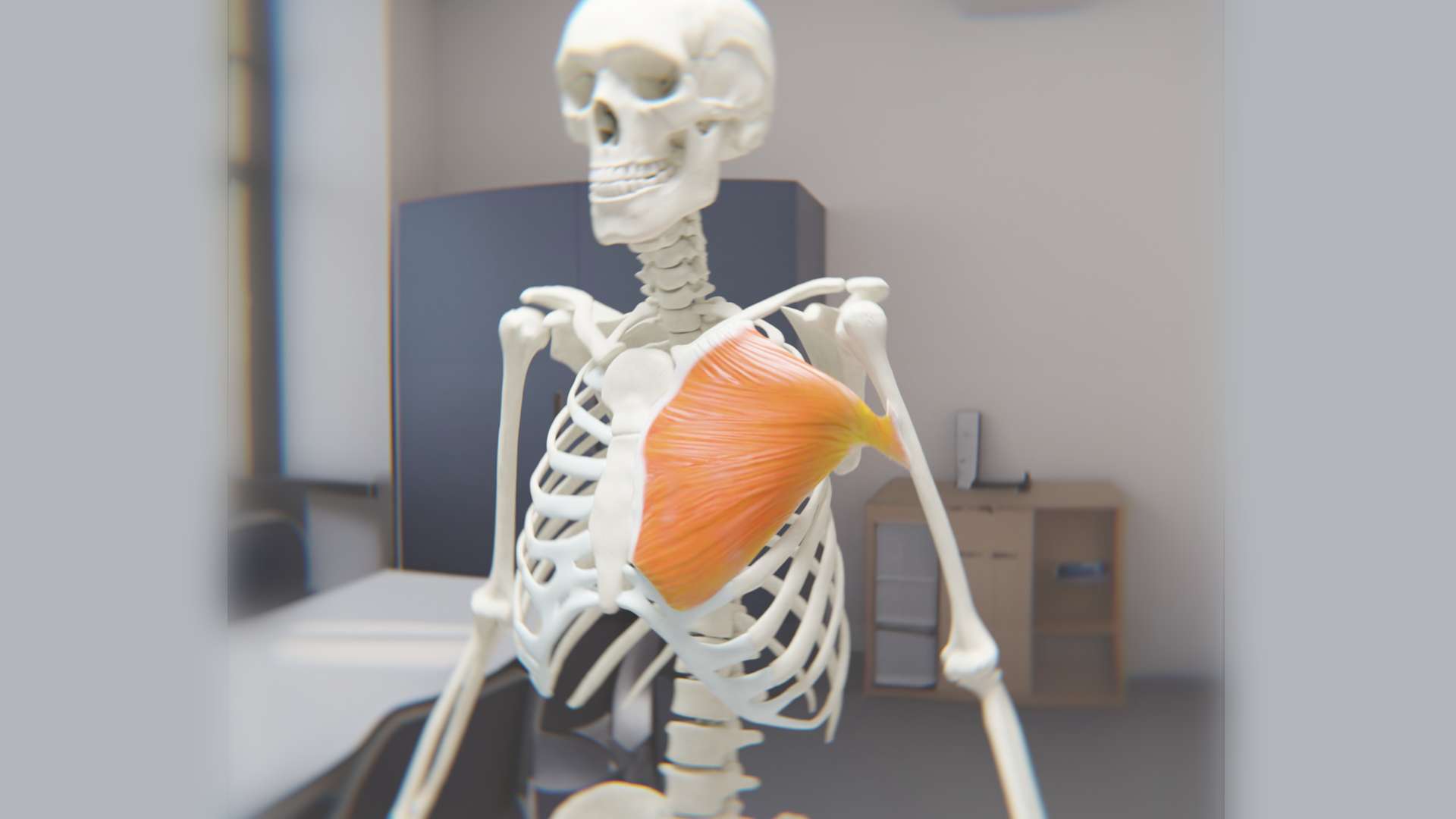
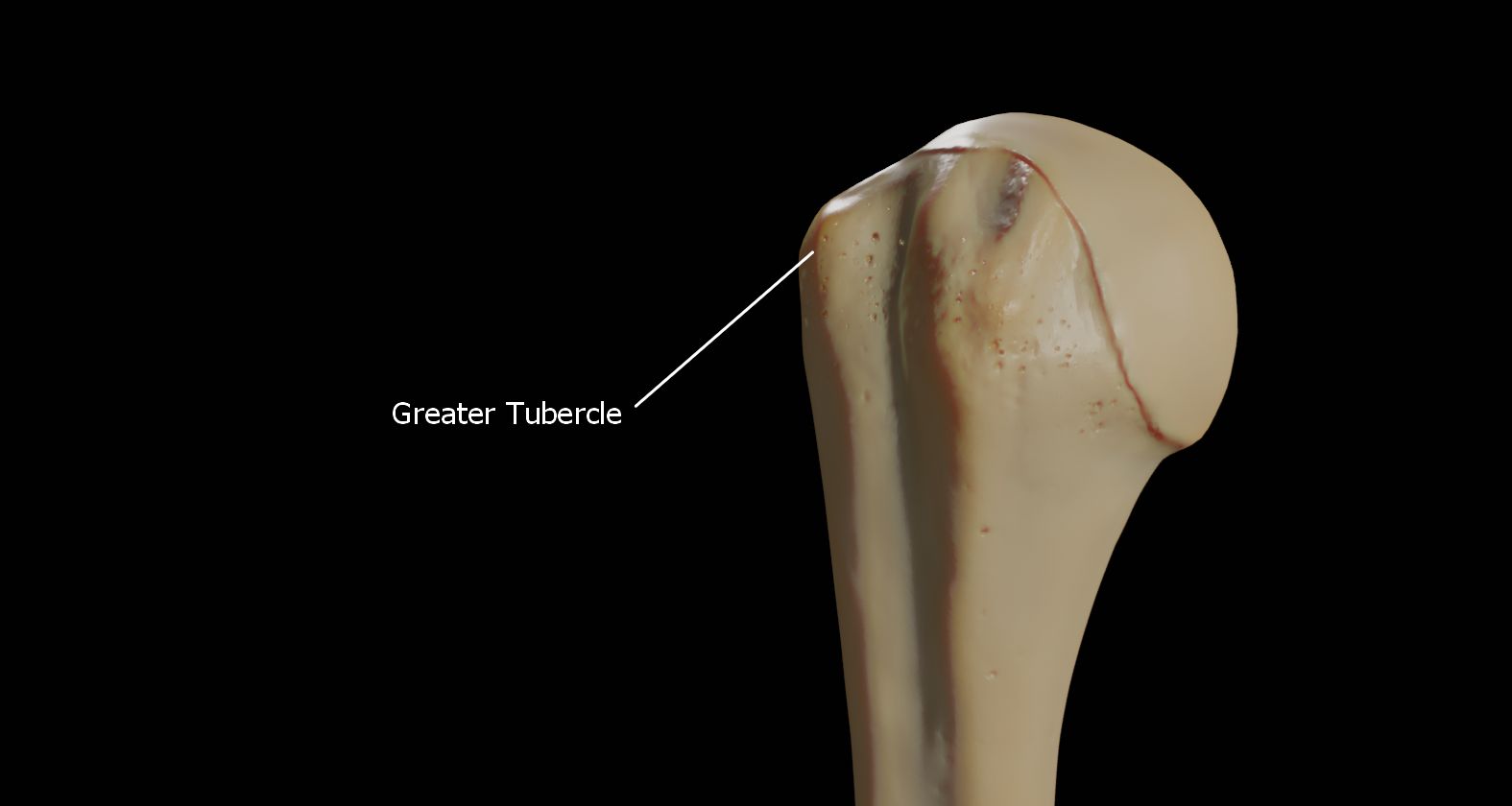
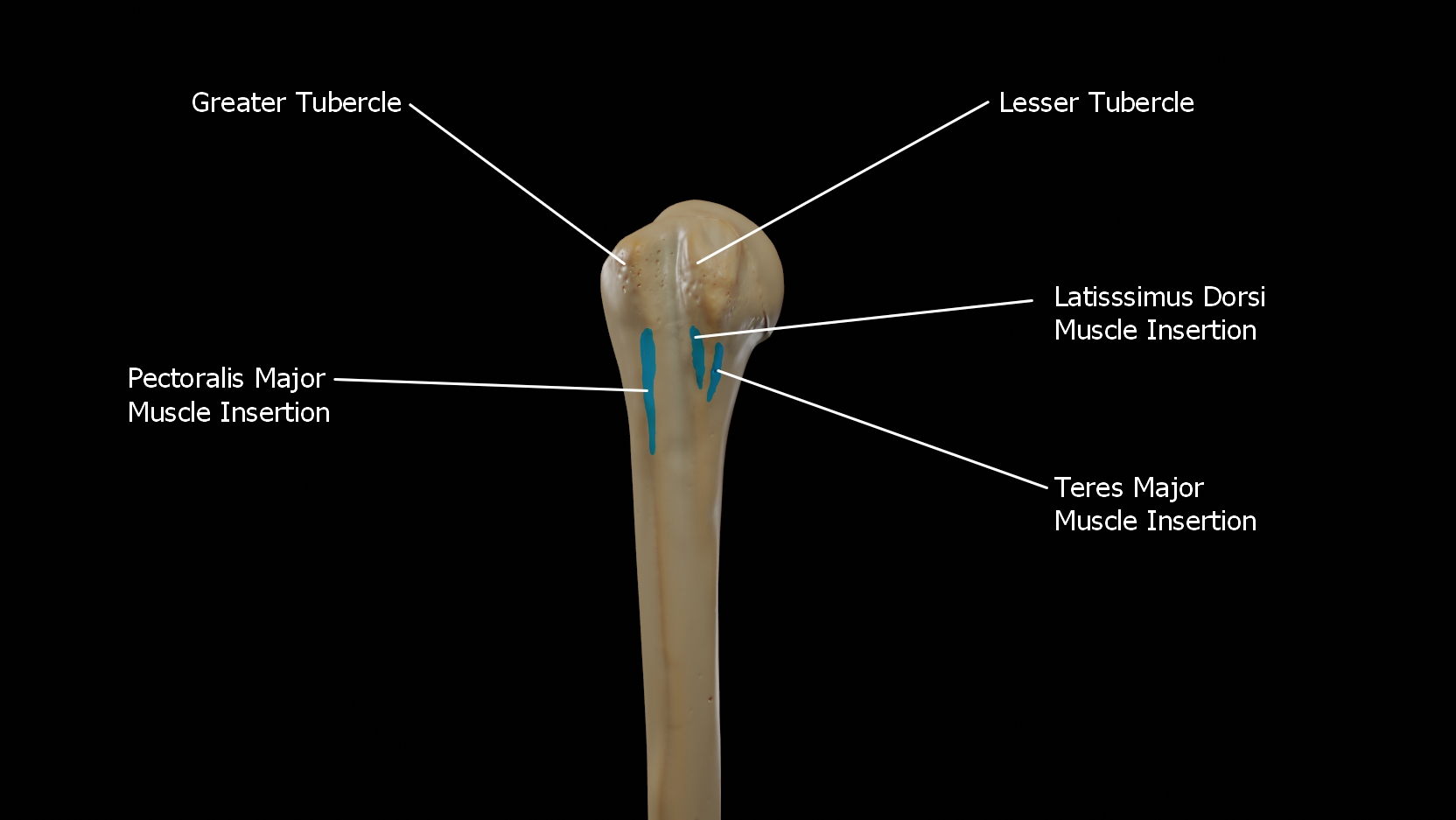
The Greater Tubercle
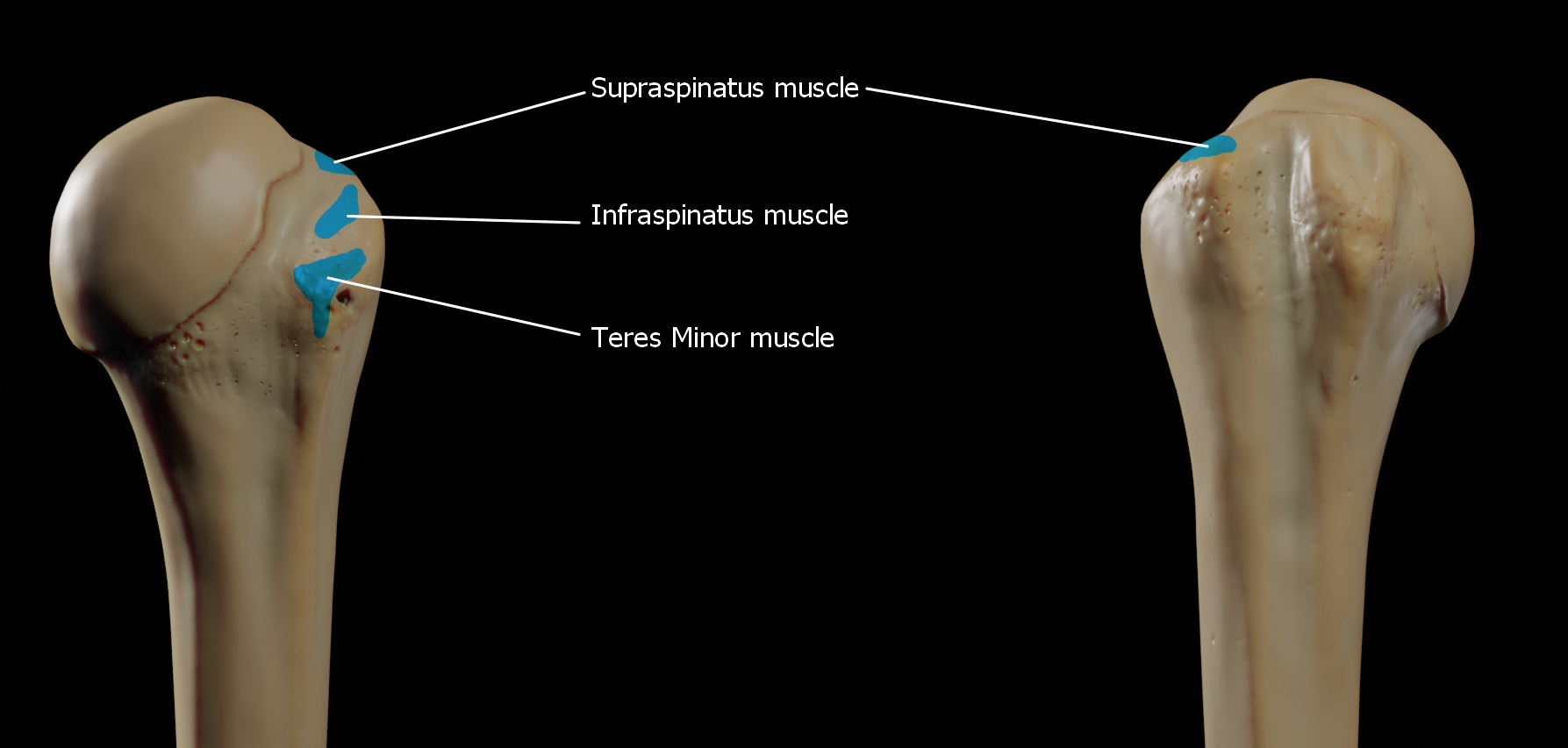
The greater tubercle is a large, posteriorly placed projection that is placed laterally. The greater tubercle is where supraspinatus, infraspinatus and teres minor muscles are attached.
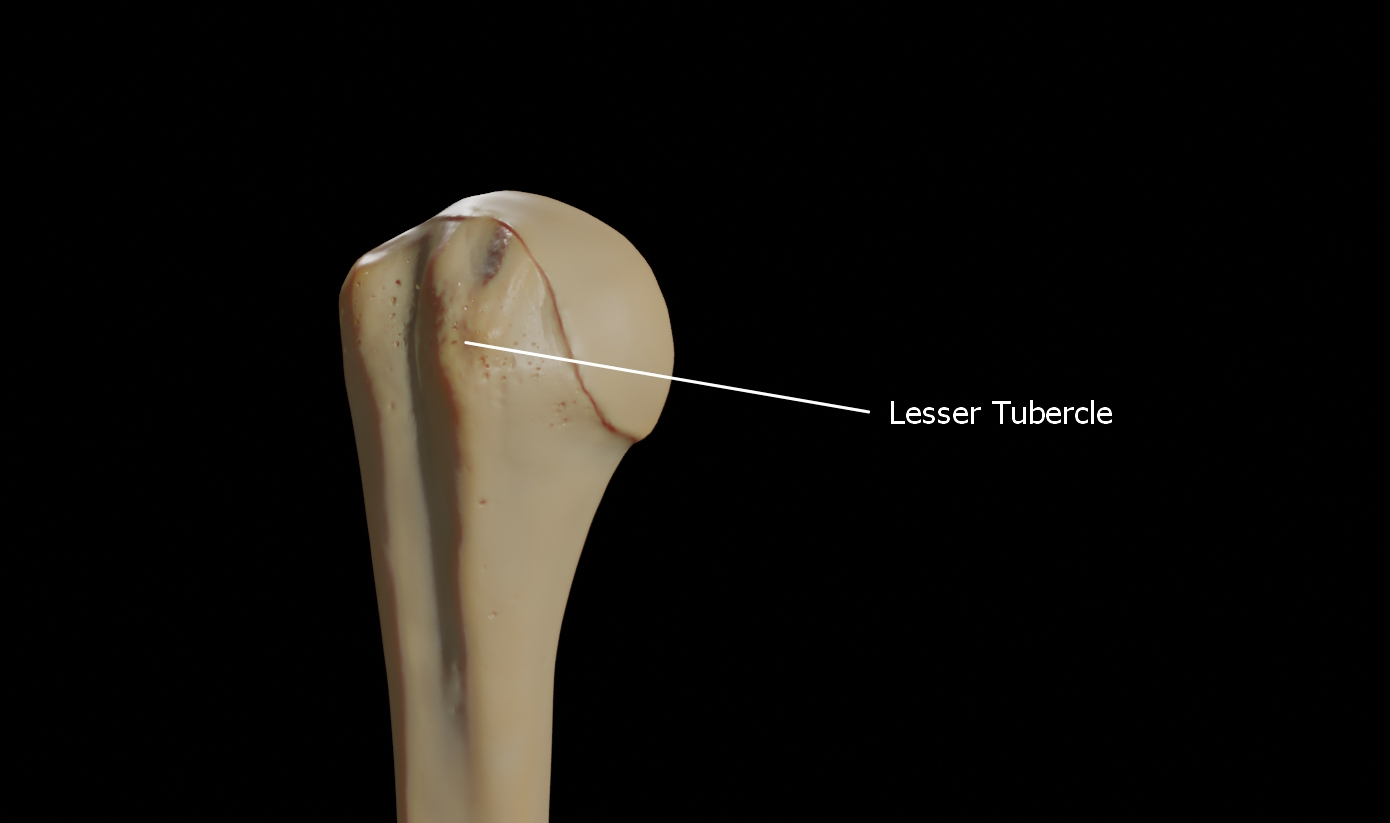
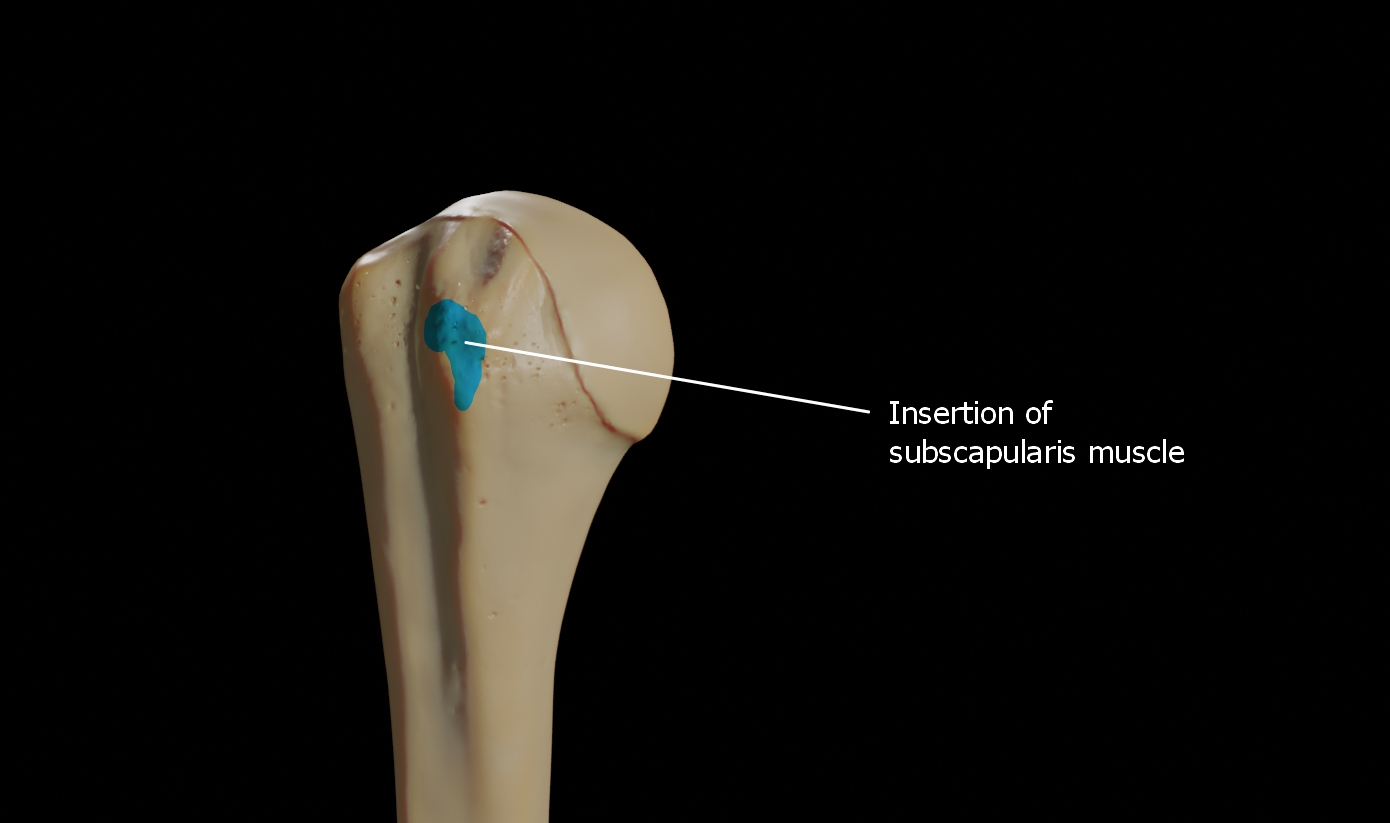
The Lesser Tubercle
The lesser tubercle is smaller, anterolaterally placed to the head of the humerus. The lesser tubercle provides insertion to subscapularis muscle. Both these tubercles are found in the proximal part of the shaft.
The Bicipital Sulcus
The intertubercular groove or also known as the bicipital sulcus is a deep groove that begins between the two tubercles and extends longitudinally down the proximal shaft of the humerus.
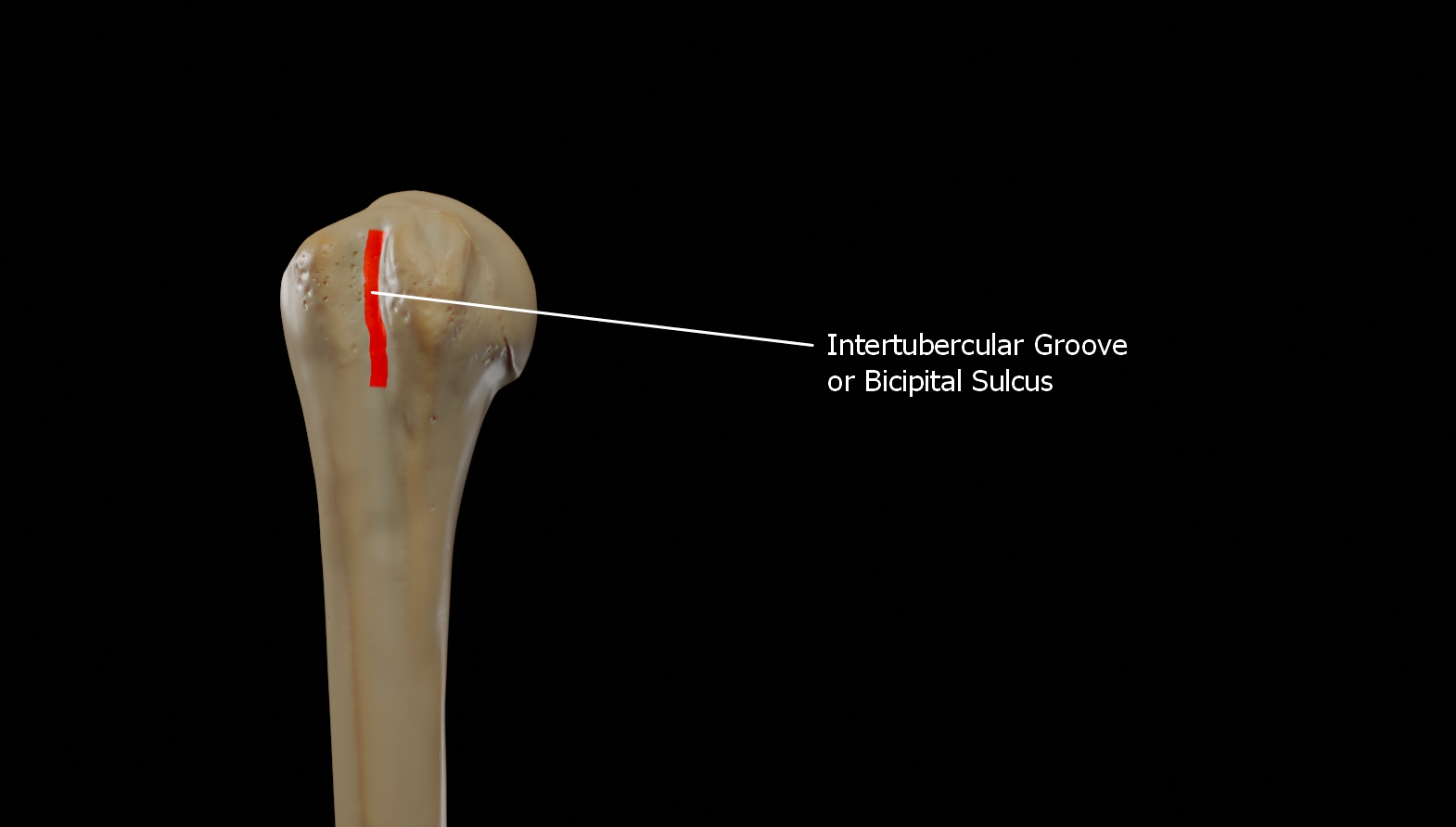
The long head of biceps brachii muscle runs along this groove. The transverse humeral ligament connects the lesser and greater tubercles and bridges this groove to form a canal.
Crest of Greater Tubercle
This crest forms the lateral lip of the bicipital groove and is the site for insertion of pectoralis major.
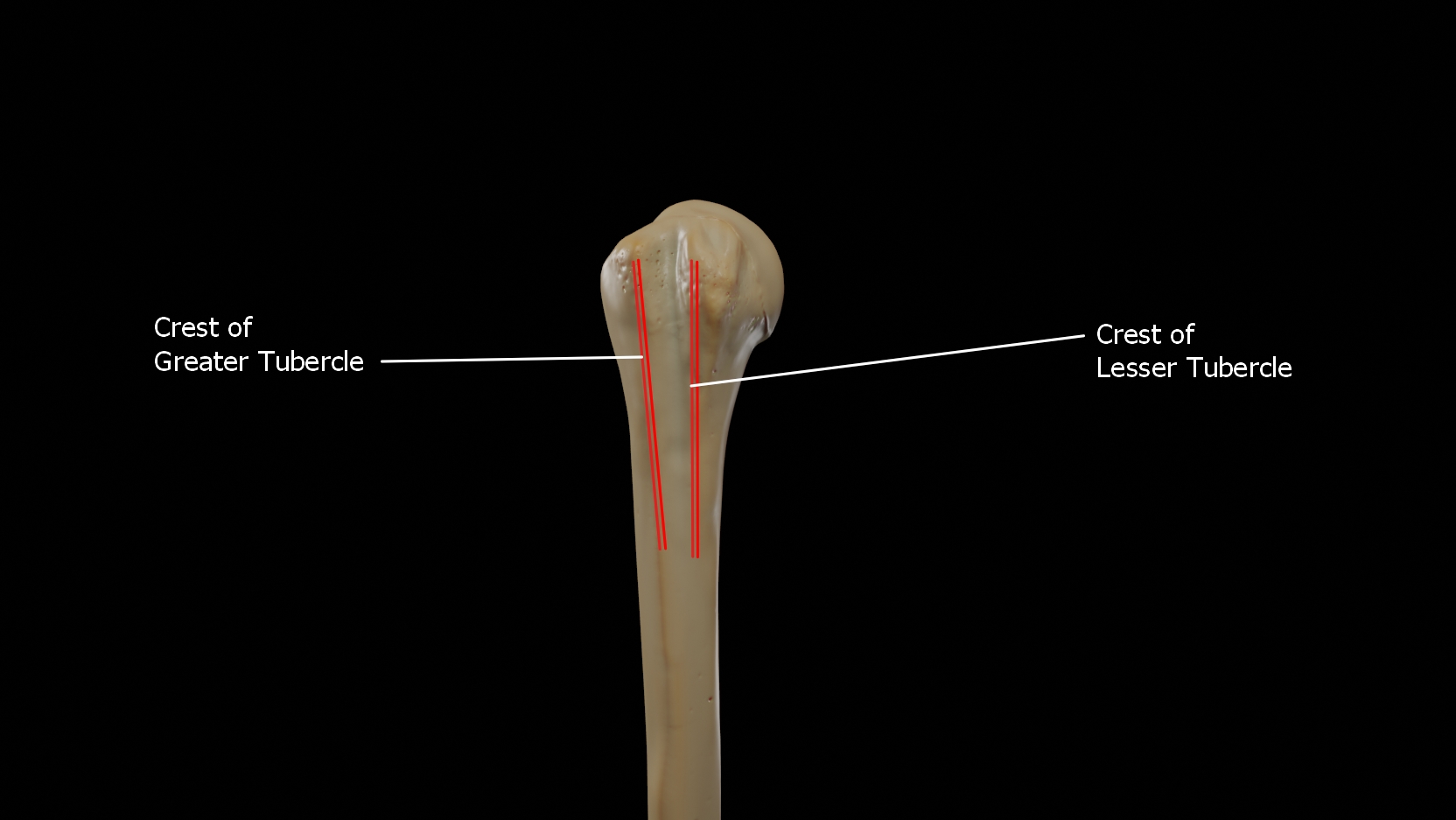
Crest of Lesser Tubercle
This crest forms the medial lip of the bicipital groove and is the site for insertion of teres major and latissimus dorsi muscles.
Shaft of the humerus
The shaft of the humerus is triangular to cylindrical in cut section and is compressed anteroposteriorly. It has 3 surfaces, namely:
Anteromedial Surface
This is the area between the medial border of the humerus to the line drawn as a continuation of the crest of the greater tubercle.
Anterolateral Surface
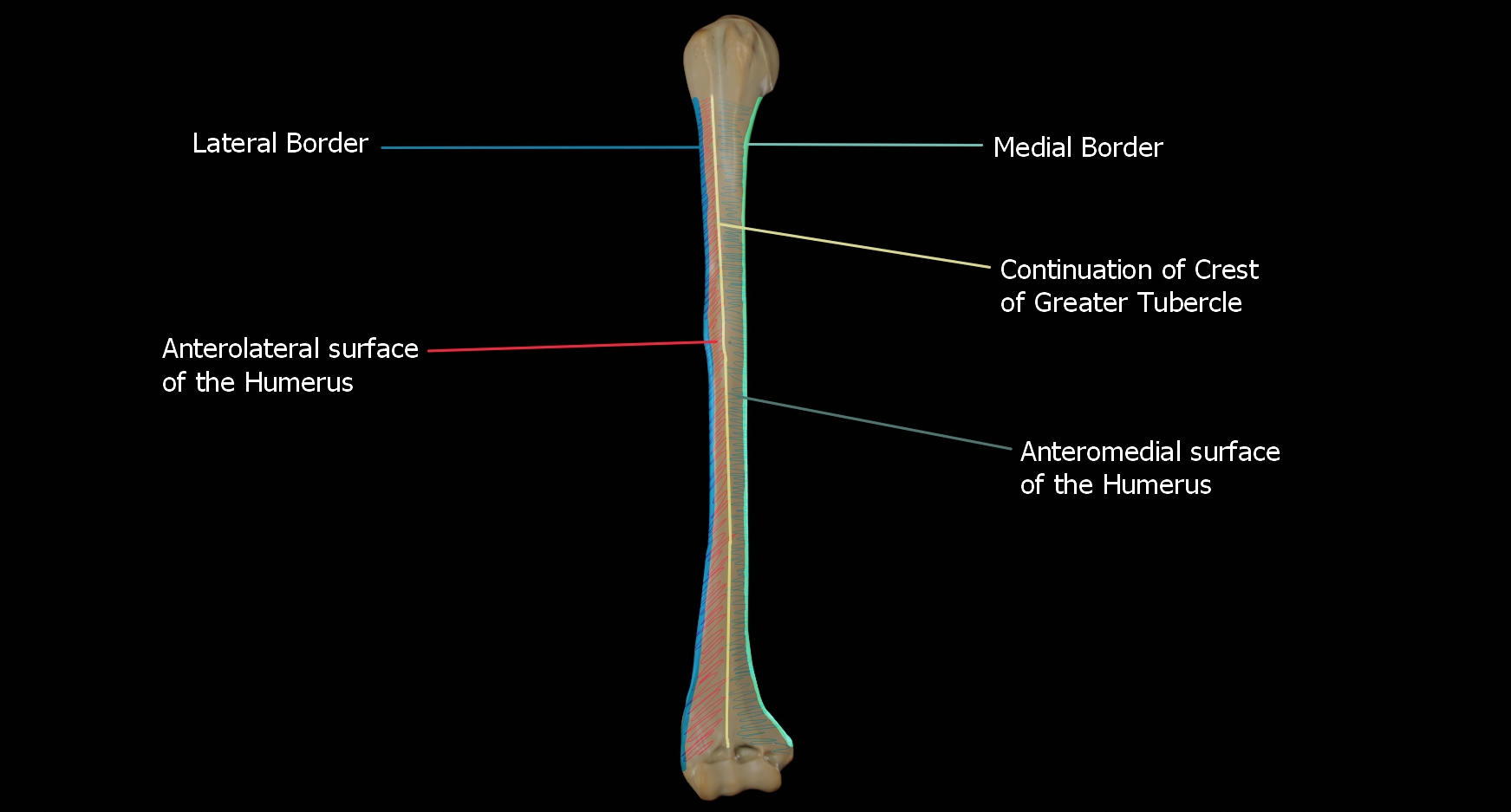
This is the area between the lateral border of the humerus to the line drawn as a continuation of the crest of the greater tubercle.
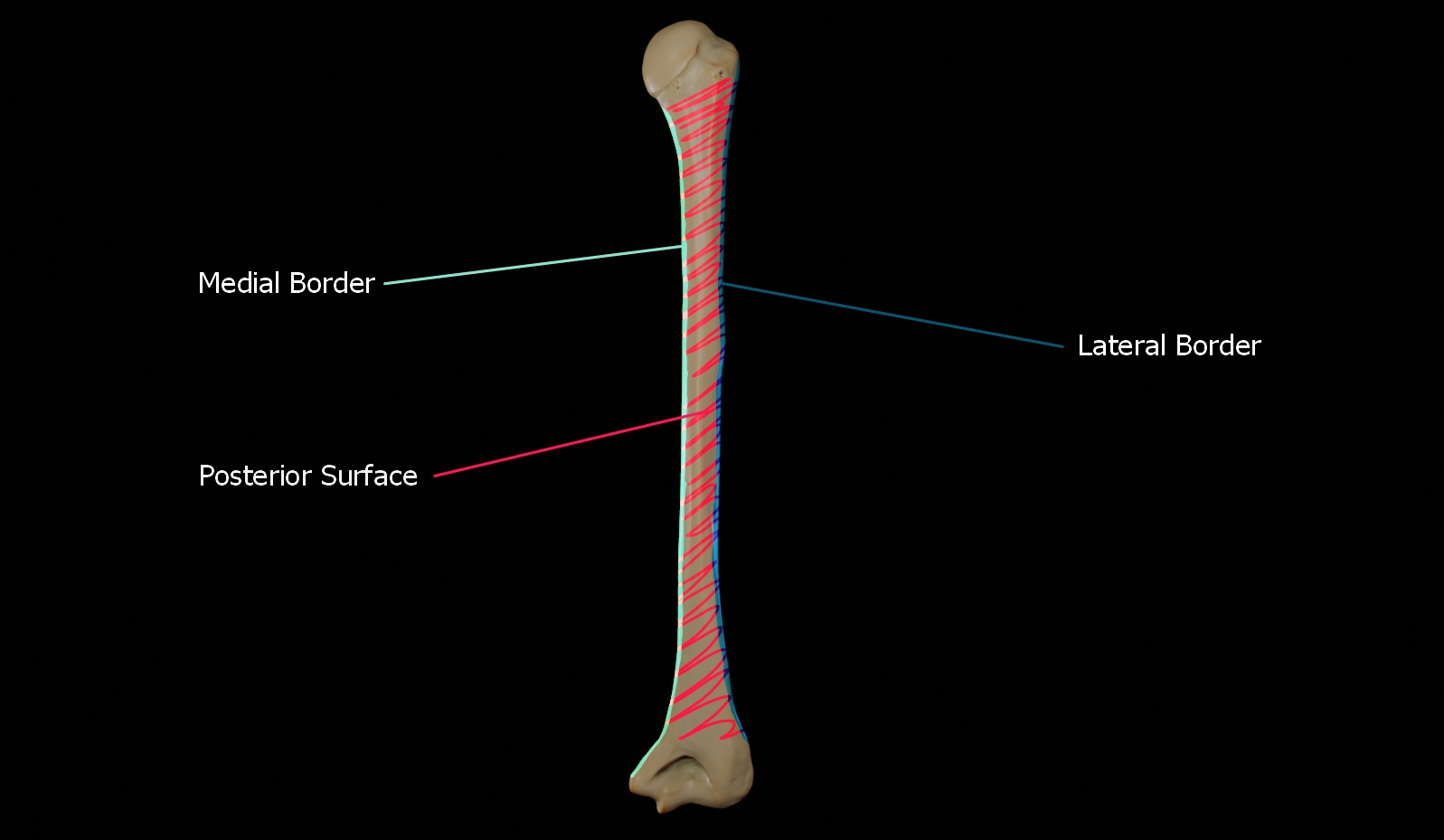
Posterior Surface
This is the area between the medial and lateral borders.
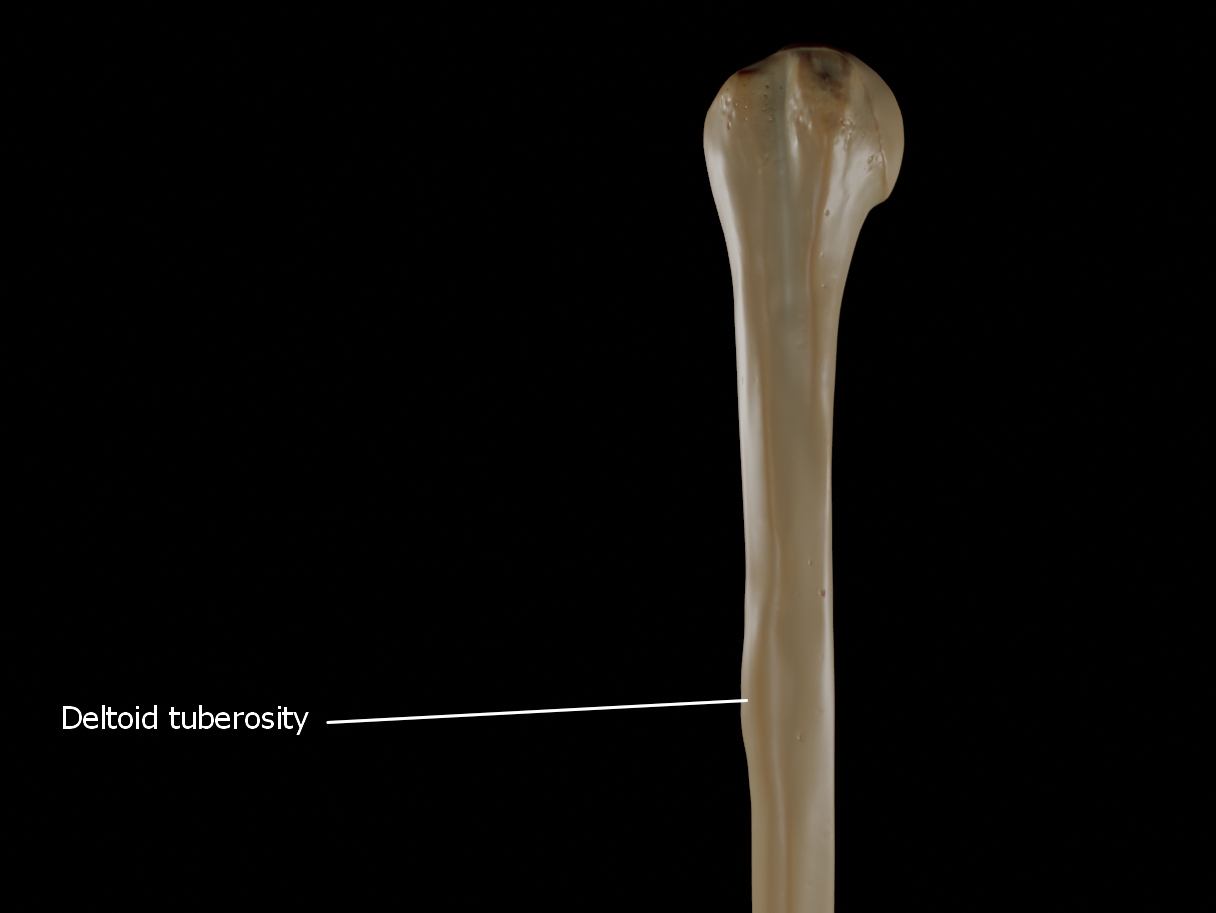
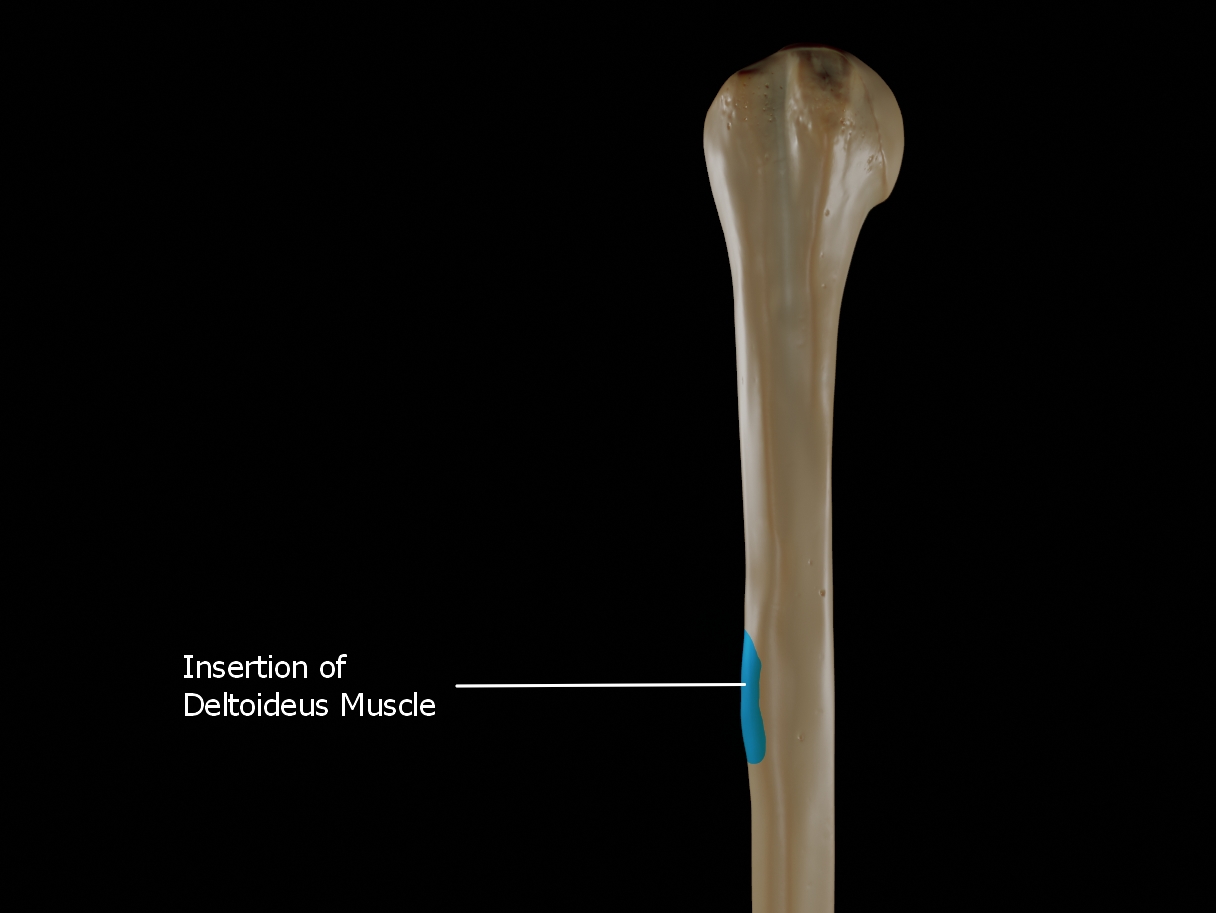
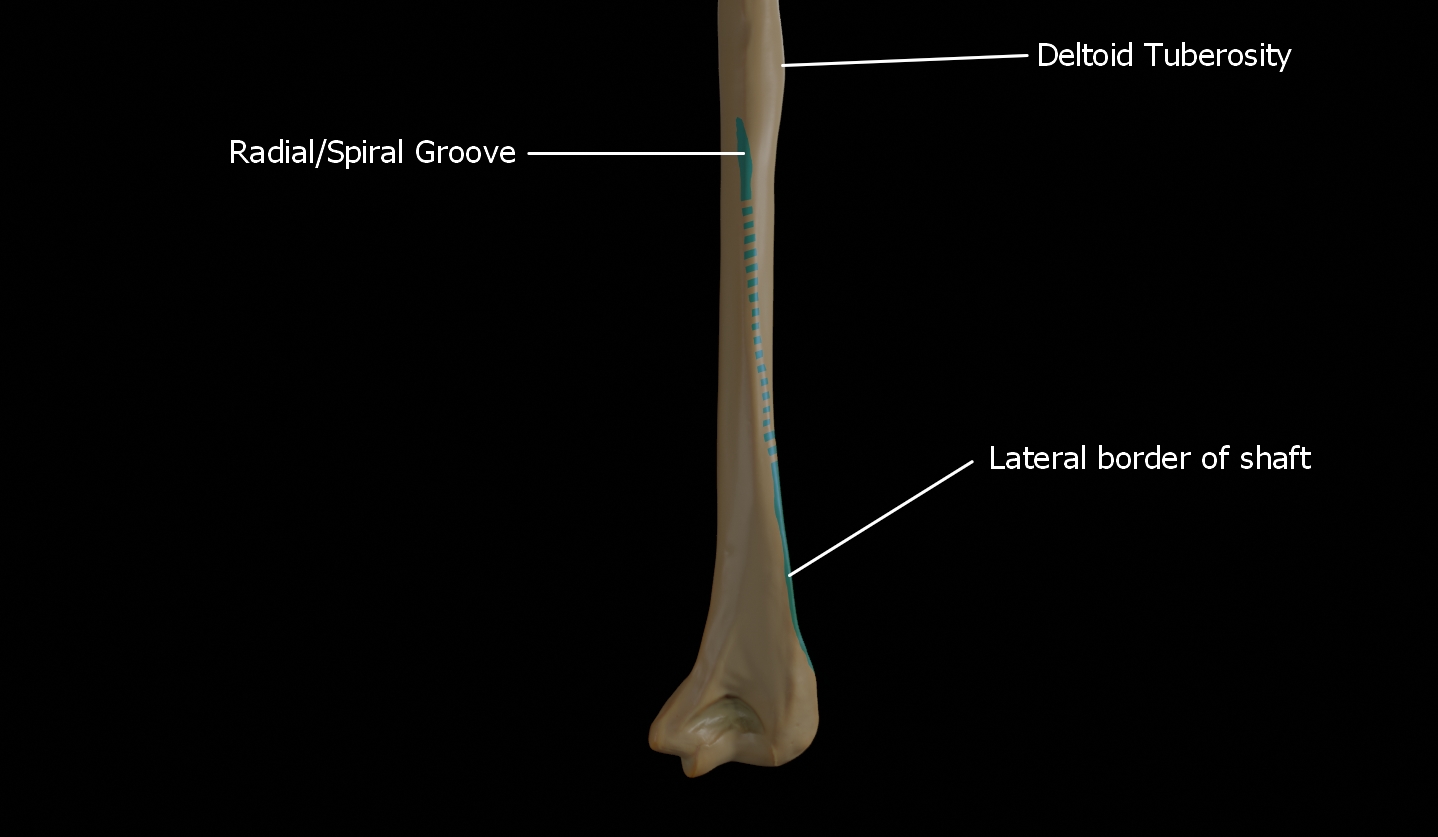
Deltoid Tuberosity
The Deltoid tuberosity is a roughened surface on the lateral surface of the shaft of the Humerus and acts as the site of insertion of deltoideus muscle.
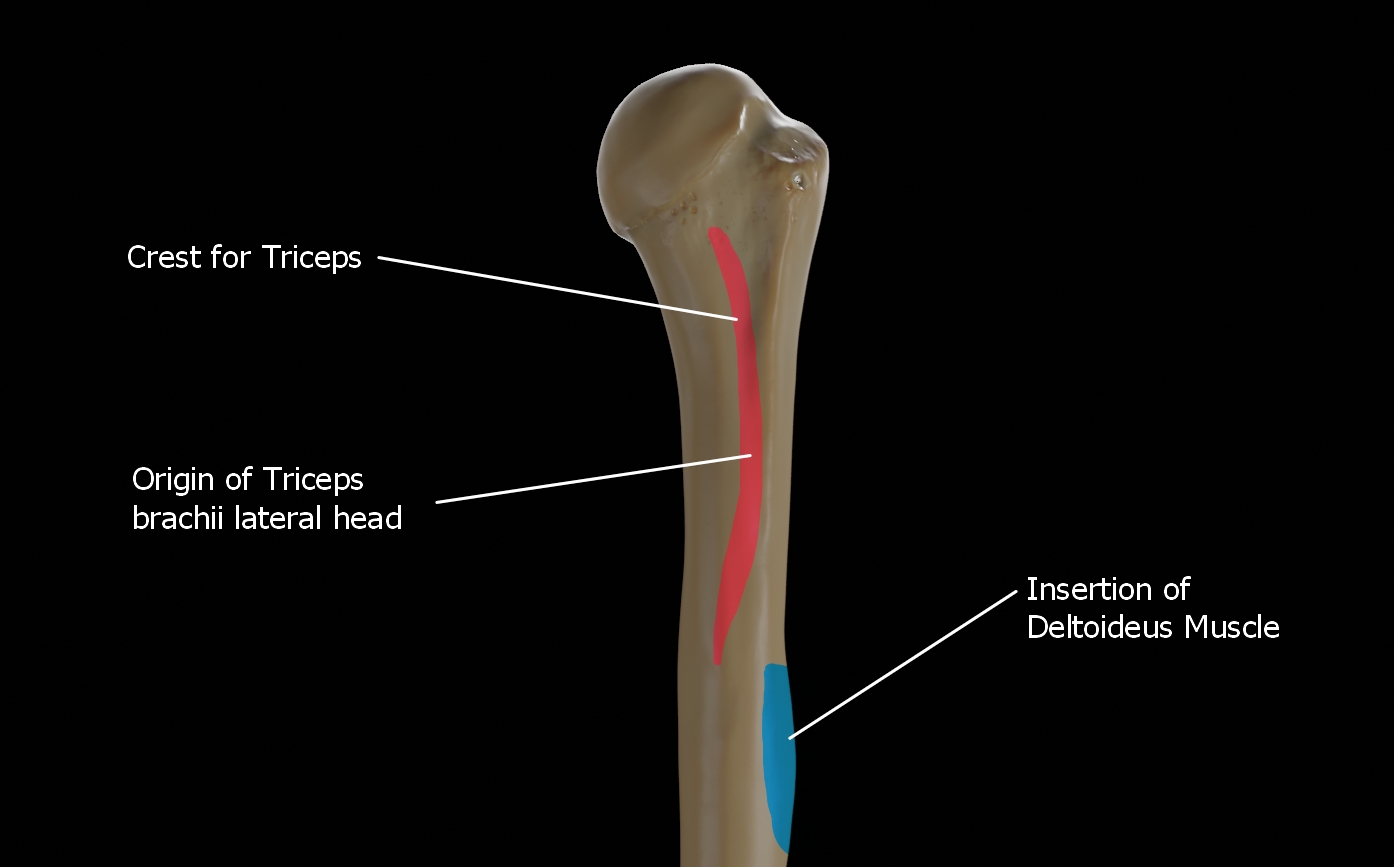
Crest for triceps brachii
The posterorsuperior part of the shaft has a crest, beginning just below the surgical neck of the humerus and extends till the superior tip of the deltoid tuberosity. This is where the lateral head of triceps brachii is attached.
Spiral groove
The radial sulcus, also known as the spiral groove is found on the posterior surface of the shaft and is a shallow oblique groove through which the radial nerve passes along with deep vessels. This is located posteroinferior to the deltoid tuberosity. The inferior boundary of the spiral groove is continuous distally with the lateral border of the shaft.
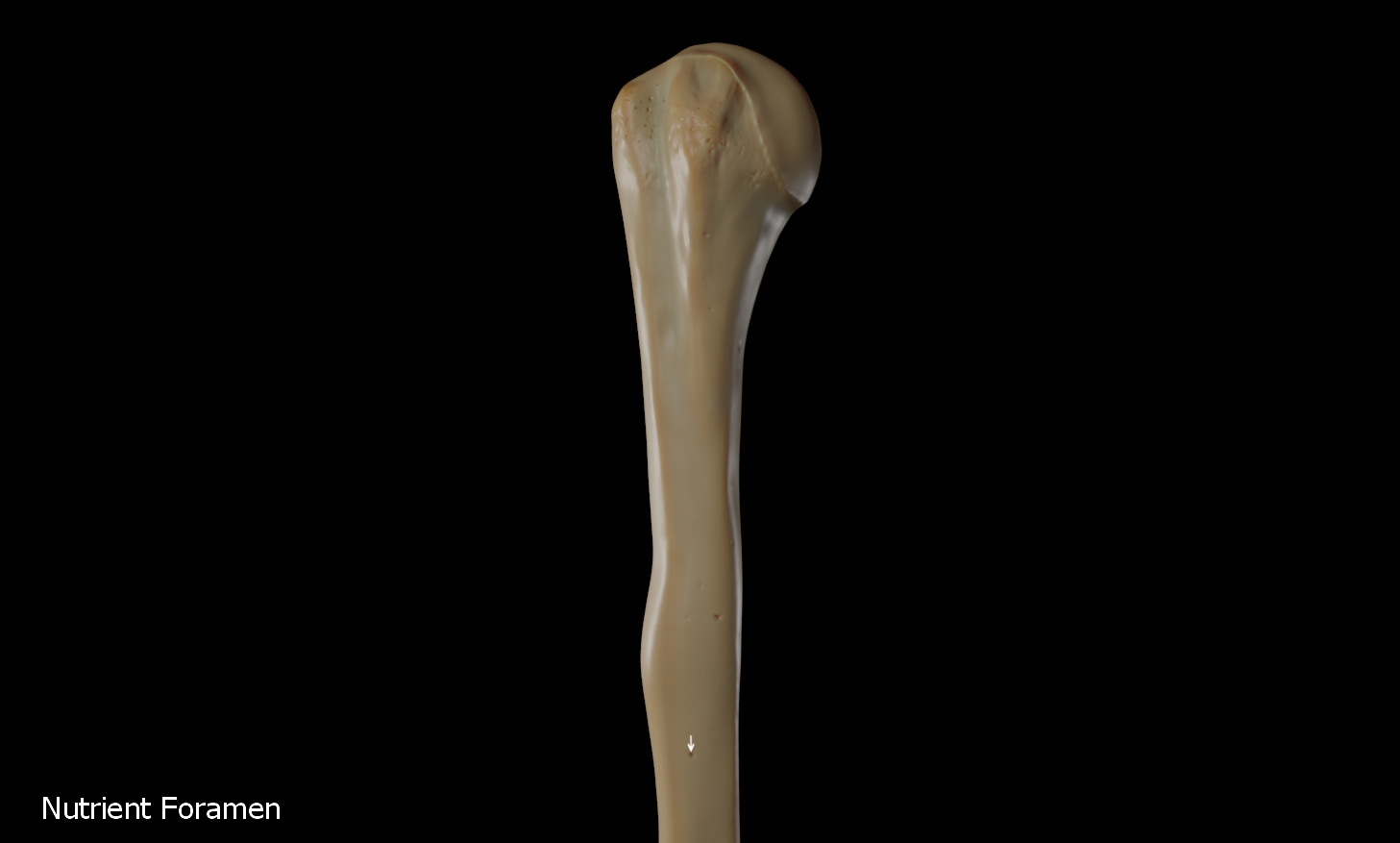
Nutrient foramen
The nutrient foramen of the humerus is located in the anteromedial surface of the humerus. The nutrient arteries enter the humerus through this foramen.
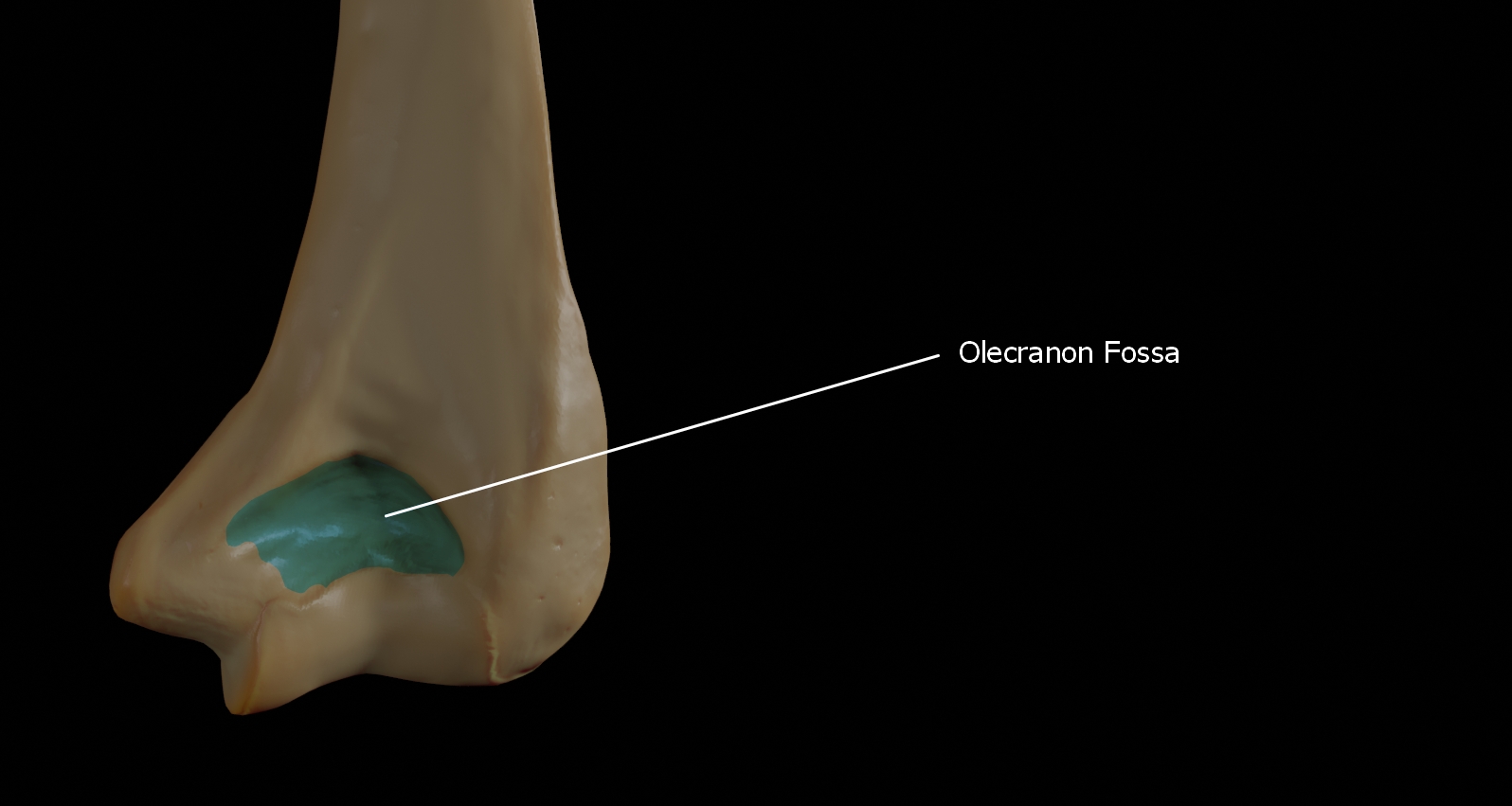
Olecranon Fossa
Olecranon fossa is the posterior hollow part on the distal humerus which accommodates the olecranon process of the ulna during extension of the elbow.
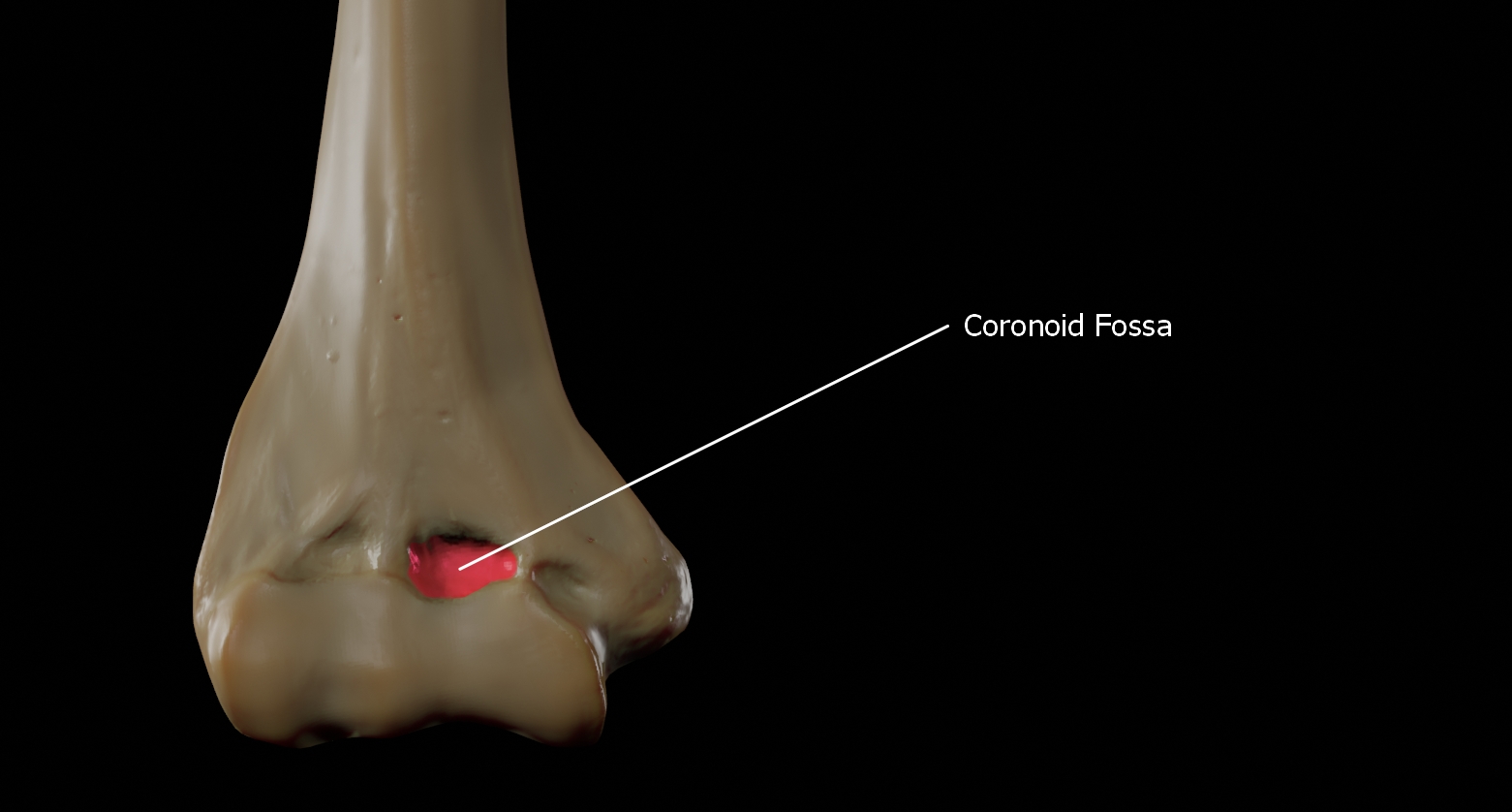
Coronoid fossa
The coronoid fossa is the medial hollow part on the anterior surface of the distal humerus. The coronoid fossa is larger than the olecranon fossa and receives the coronoid process of the ulna during maximum flexion of the elbow.
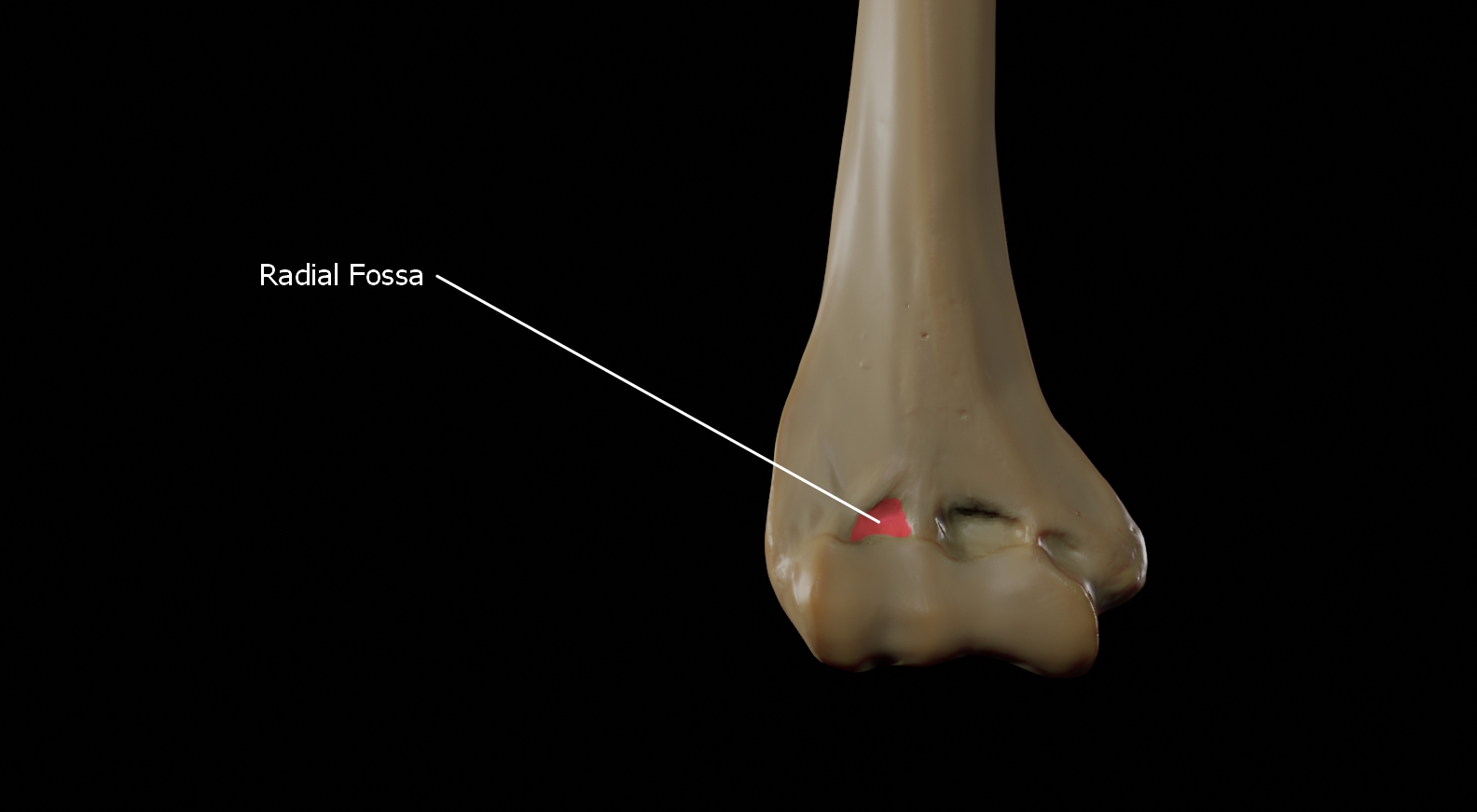
Radial fossa
The Radial fossa is located laterally on the anterior surface of the distal forearm and this part receives the head of the radius during maximum flexion of the elbow.
Capitulum
This is a rounded eminence forming the lateral part of the distal humerus. The head of the radius articulates with the capitulum.
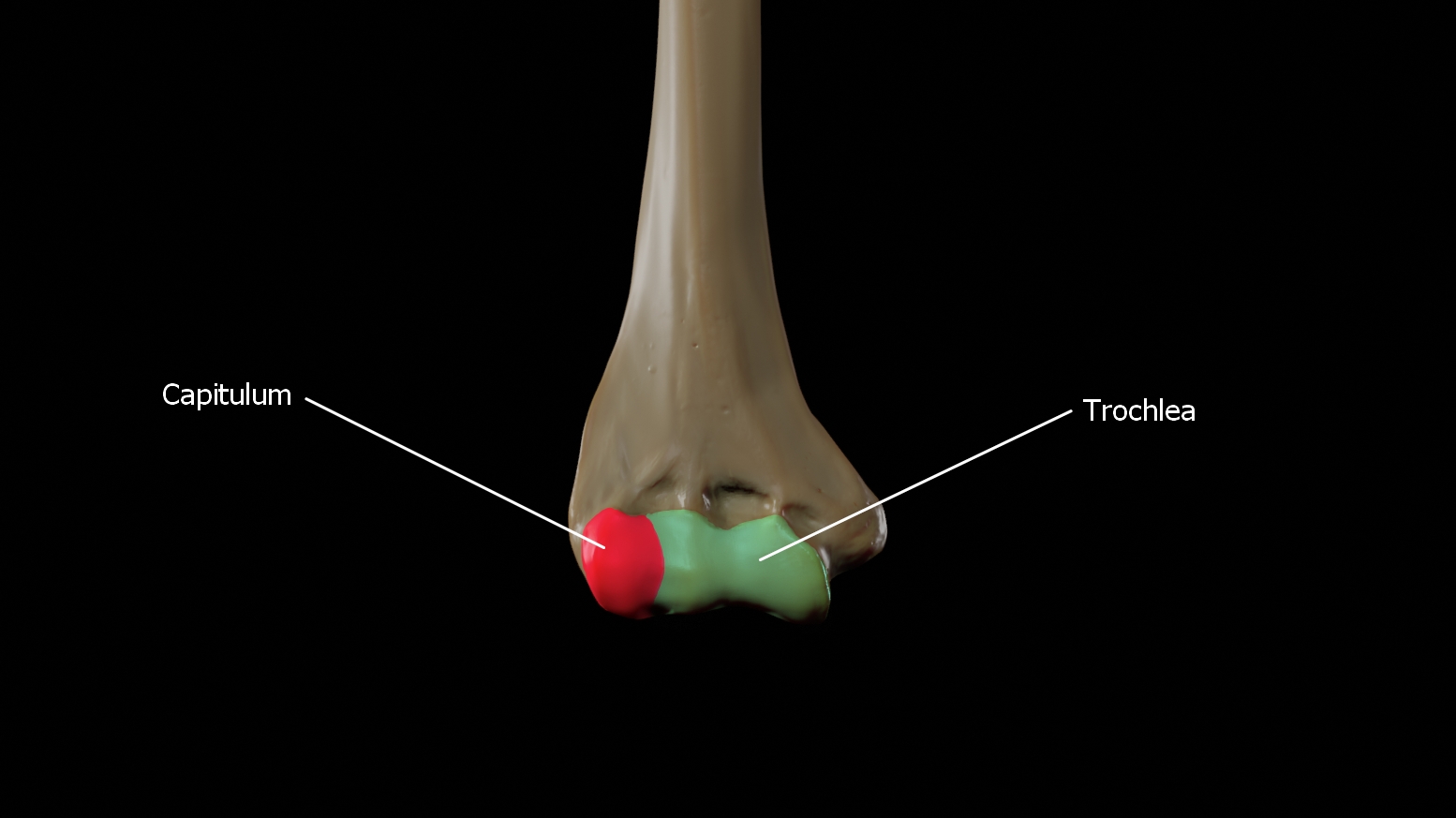
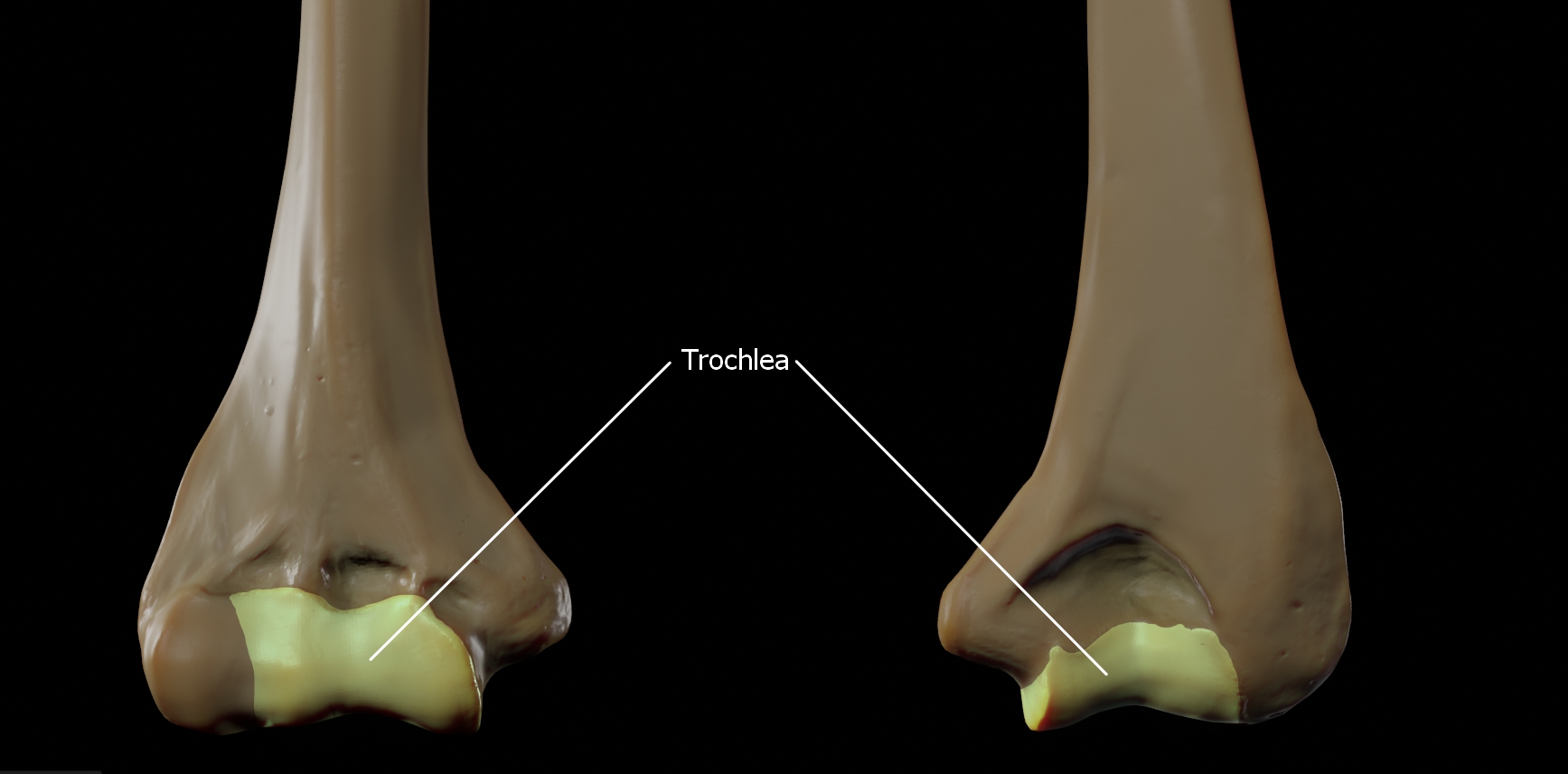
Trochlea
The trochlea is spool-shaped medial portion of the distal humerus and articulates with the ulna.
Lateral Epicondyle
The lateral epicondyle is the non-articular lateral bulge of bone located superior and lateral to the capitulum. The radial collateral ligament attaches to the lateral epicondyle. The common tendon of the extensor muscles of the forearm and the supinator muscle originate on the lateral collateral ligament.
![]()
Medial Epicondyle
The medial epicondyle is the non-articular medial bulge of bone located superior and medial to the trochlea. The medial epicondyle is more prominent than the lateral epicondyle and the ulnar collateral ligament is attached here along with the forearm flexors.
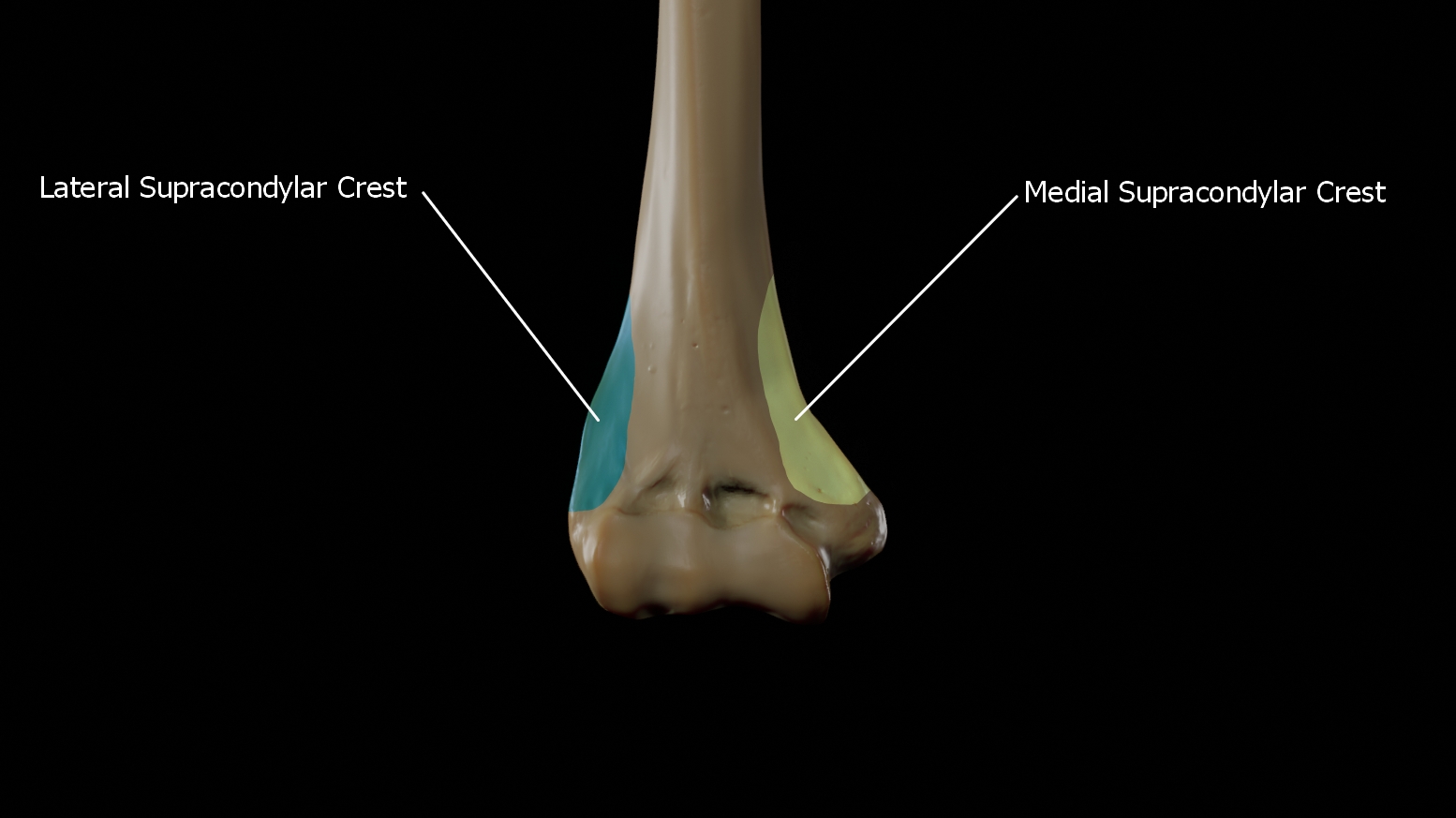
Medial supracondylar crest
This forms the sharp medial border of the distal humerus continuing superiorly from the medial epicondyle.
Lateral supracondylar crest
This forms the sharp lateral border of the distal humerus continuing superiorly from the lateral epicondyle.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.